MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS
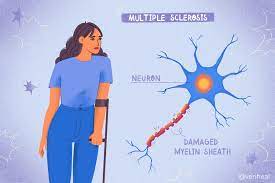
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic neurological disorder that affects the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord. It is characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking the protective covering of nerve fibers, called myelin, causing inflammation and damage. This disrupts the normal flow of electrical impulses along the nerves, leading to a wide range of symptoms.
CAUSES OF MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS
The exact cause of multiple sclerosis is not known, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. MS is more common in women than men and is typically diagnosed between the ages of 20 and 50, although it can occur at any age.
TYPES OF MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS
There are different types of multiple sclerosis, including relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS), primary progressive MS (PPMS), secondary progressive MS (SPMS), and progressive-relapsing MS (PRMS). RRMS is the most common type, characterized by periods of relapse (worsening of symptoms) followed by periods of remission (partial or complete recovery). PPMS involves a gradual worsening of symptoms without distinct relapses or remissions. SPMS starts as RRMS and later transitions into a progressive phase with a gradual worsening of symptoms. PRMS is the least common type and involves a steady worsening of symptoms with occasional relapses.
SYMPTOMS OF MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS
Symptoms of multiple sclerosis can vary widely among individuals and depend on the location and extent of the damage in the CNS. Some common symptoms include fatigue, difficulty walking, muscle weakness, numbness or tingling, problems with coordination and balance, visual disturbances, bladder and bowel dysfunction, cognitive changes, and emotional disturbances.
TREATMENT OF MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS
There is no cure for multiple sclerosis, but various treatment options are available to manage the symptoms, slow down the progression of the disease, and improve quality of life. These include medications to reduce inflammation and modify the immune system response, physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and lifestyle modifications. In recent years, there have been advancements in disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) that have shown promise in slowing disease progression and reducing relapses in individuals with MS.
It’s important for individuals with multiple sclerosis to work closely with healthcare professionals, including neurologists and other specialists, to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals. Support from family, friends, and support groups can also play a crucial role in managing the challenges of living with MS.
There are several treatment options available to manage the symptoms of multiple sclerosis, slow down disease progression, and improve quality of life. These include:
-
Disease-modifying therapies (DMTs): DMTs are medications that can help slow down the progression of MS by reducing inflammation, suppressing the immune system, or targeting specific aspects of the disease. There are several DMTs available, including injectable medications, oral medications, and infusion therapies. The choice of DMT depends on various factors such as the type of MS, disease activity, and individual patient characteristics. It is important to work with a neurologist or healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate DMT for each individual.
-
Symptom management medications: Depending on the specific symptoms experienced, various medications can be prescribed to manage MS symptoms. For example, medications such as muscle relaxants can help with muscle stiffness and spasms, pain medications can alleviate pain, and antidepressants can assist with mood and emotional disturbances. Medications may also be prescribed for bladder and bowel dysfunction, fatigue, and other symptoms.
-
Rehabilitation therapies: Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy can be beneficial for individuals with MS. Physical therapy aims to improve strength, flexibility, balance, and mobility, while occupational therapy helps individuals adapt to any limitations in daily activities. Speech therapy can address speech and swallowing difficulties. Rehabilitation therapies can enhance functional abilities, improve overall well-being, and manage specific symptoms.
-
Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can have a positive impact on MS management. Regular exercise, when appropriate, can help improve strength, endurance, and mood. A well-balanced diet can support overall health and may include specific recommendations, such as maintaining adequate vitamin D levels. Stress management techniques, such as relaxation exercises or mindfulness practices, may also be beneficial. It is important to discuss lifestyle modifications with healthcare professionals to ensure they are suitable for individual needs.
-
Symptom-specific interventions: Depending on the symptoms experienced, additional interventions may be recommended. For example, medications can be prescribed for bladder dysfunction or spasticity. Assistive devices like canes, braces, or wheelchairs can assist with mobility. Visual aids, such as magnifiers, may be beneficial for individuals with vision problems. Cognitive rehabilitation programs can help manage cognitive changes.
-
Emotional and psychological support: Living with MS can be challenging emotionally and psychologically. Support from mental health professionals, counselors, or support groups can provide coping strategies, emotional support, and a safe space to discuss concerns. Managing stress and maintaining a positive outlook can also contribute to overall well-being.
It is essential for individuals with MS to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals. Regular communication and monitoring of the disease’s progression can help ensure that the treatment plan remains effective and appropriate over time.